Intel Xeon E-2286G Benchmarks
For this exercise, we are using our legacy Linux-Bench scripts which help us see cross-platform “least common denominator” results we have been using for years as well as several results from our updated Linux-Bench2 scripts. At this point, our benchmarking sessions take days to run and we are generating well over a thousand data points. We are also running workloads for software companies that want to see how their software works on the latest hardware. As a result, this is a small sample of the data we are collecting and can share publicly. Our position is always that we are happy to provide some free data but we also have services to let companies run their own workloads in our lab, such as with our DemoEval service. What we do provide is an extremely controlled environment where we know every step is exactly the same and each run is done in a real-world data center, not a test bench.
We are going to show off a few results, and highlight a number of interesting data points in this article.
Python Linux 4.4.2 Kernel Compile Benchmark
This is one of the most requested benchmarks for STH over the past few years. The task was simple, we have a standard configuration file, the Linux 4.4.2 kernel from kernel.org, and make the standard auto-generated configuration utilizing every thread in the system. We are expressing results in terms of compiles per hour to make the results easier to read:
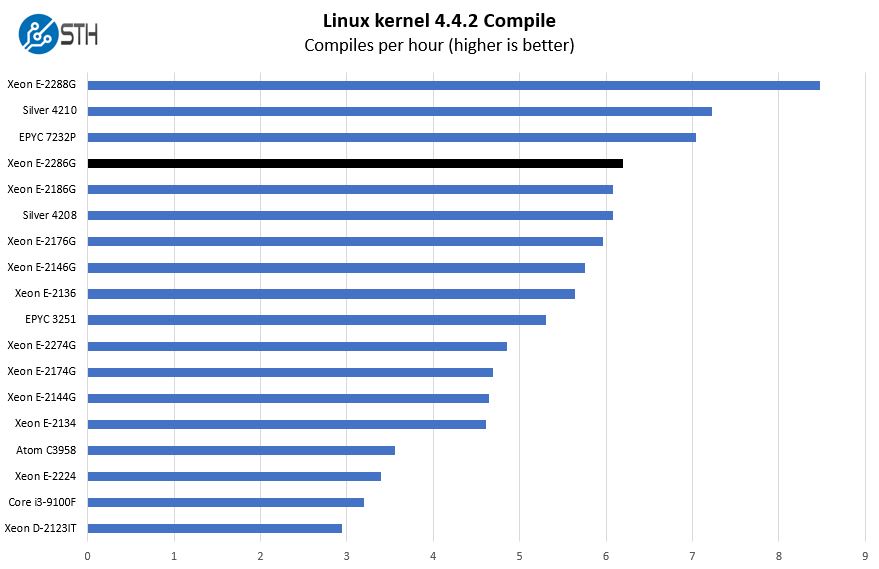
Here we see a trend that is going to continue throughout our benchmarks. The Intel Xeon E-2286G is slightly faster than the Xeon E-2186G at the same price point. That is a great result, but it is also about what we would expect here from a 200MHz base and turbo clock increase. One would not call these earth-shattering results by any means, but it is still more performance at the same price point.
c-ray 1.1 Performance
We have been using c-ray for our performance testing for years now. It is a ray tracing benchmark that is extremely popular to show differences in processors under multi-threaded workloads. We are going to use our 8K results which work well at this end of the performance spectrum.
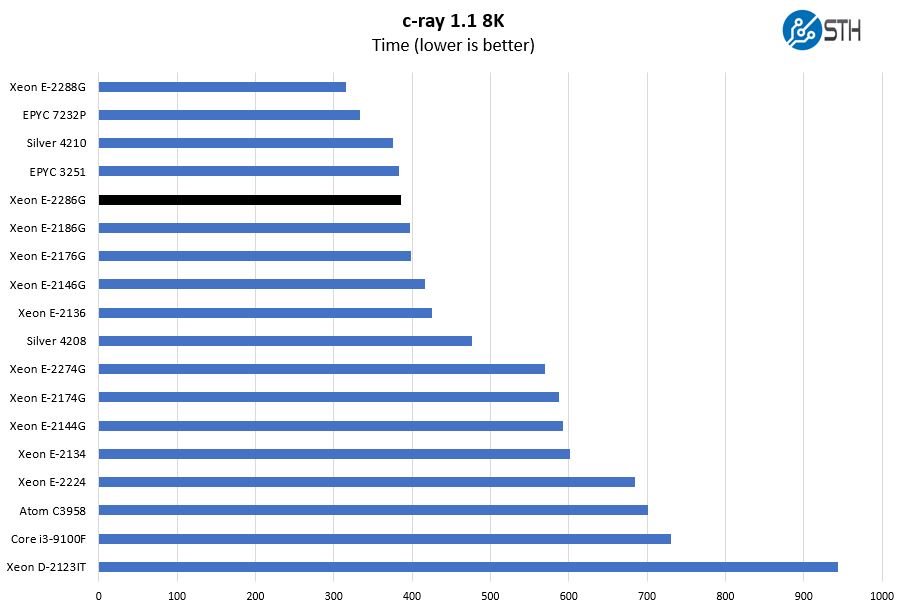
On our c-ray benchmark, we see all of the 6-core Intel Xeon E-2100 and E-2200 CPUs we tested thus far in a tight group. As much as the E-2286G has a lead over the E-2186G, the E-2186G has a slight lead over the E-2716G. This is a finely segmented SKU stack.
7-zip Compression Performance
7-zip is a widely used compression/ decompression program that works cross-platform. We started using the program during our early days with Windows testing. It is now part of Linux-Bench.
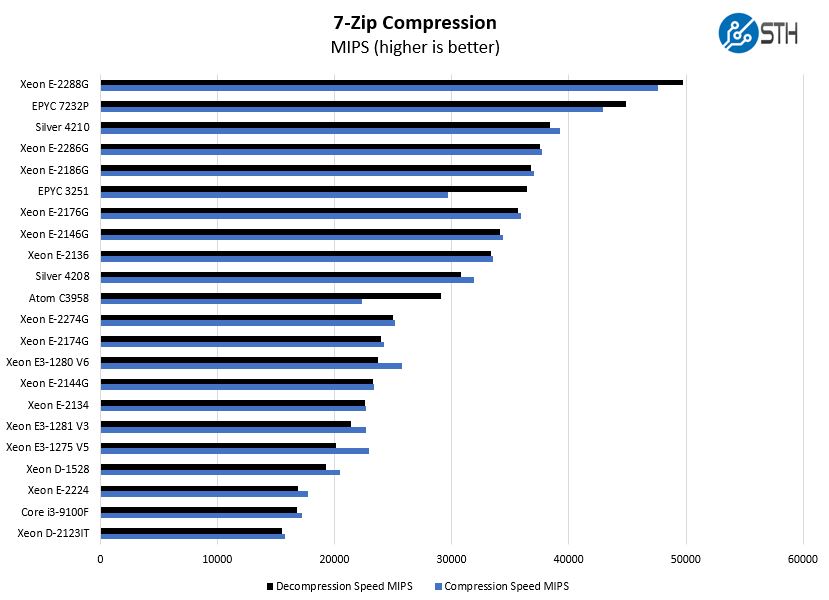
Although generationally the Xeon E-2286G is only slightly faster than its predecessor, the bigger comparison to the Intel Xeon E3-1280 V6 shows just how far these chips have come in two generations by moving from four to six cores.
NAMD Performance
NAMD is a molecular modeling benchmark developed by the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group in the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. More information on the benchmark can be found here. We are going to augment this with GROMACS in the next-generation Linux-Bench in the near future. With GROMACS we have been working hard to support Intel’s Skylake AVX-512 and AVX2 supporting AMD Zen architecture. Here are the comparison results for the legacy data set:
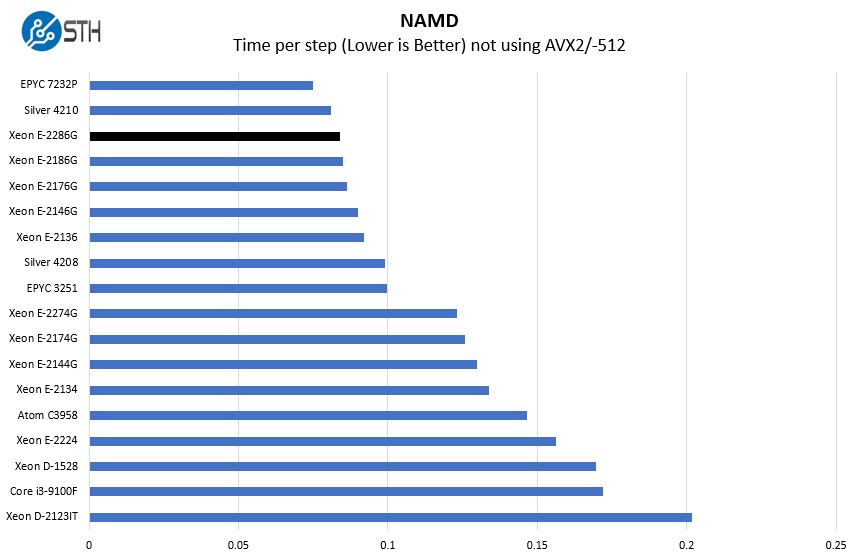
With higher clock speeds, comes more performance. The Intel Xeon E-2286G is between the Intel Xeon Silver 4208 and Intel Xeon Silver 4210 here, even at a core count deficit. Since the Intel Xeon E-2286G is also significantly less expensive, and the Xeon E server platforms are less expensive, this represents a solid cost-savings opportunity for those who can take advantage of it for lower-spec servers.
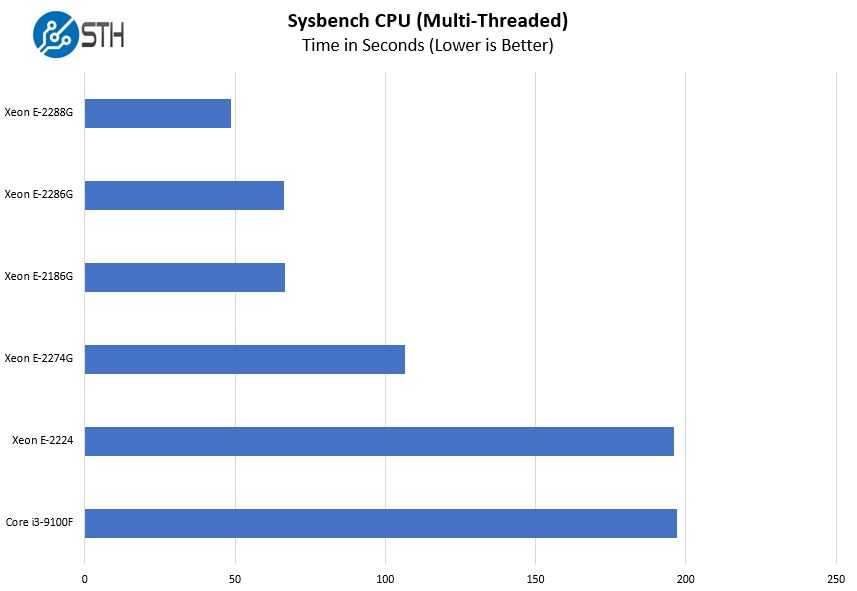
Sysbench CPU test
Sysbench is another one of those widely used Linux benchmarks. We specifically are using the CPU test, not the OLTP test that we use for some storage testing.
We also wanted to show the single-threaded results sorted by the same order as the multi-threaded results above.
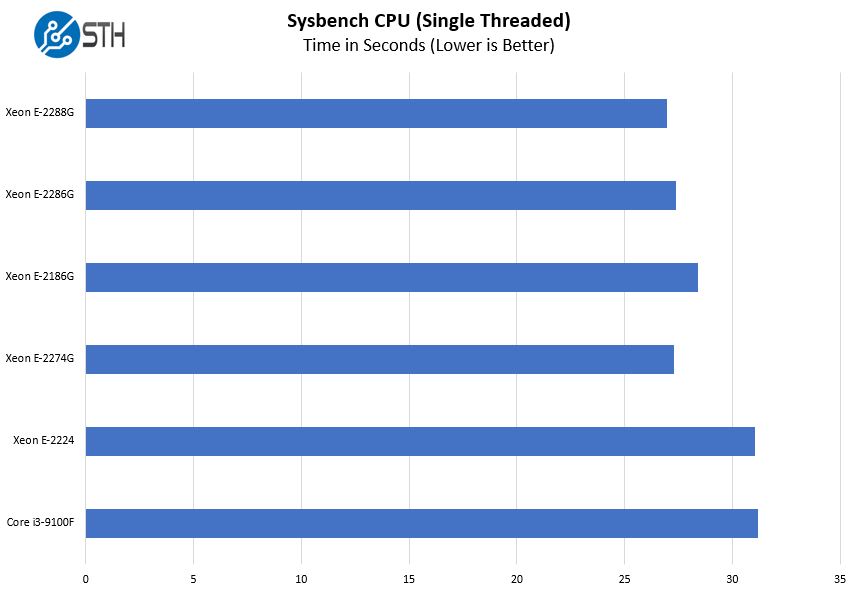
Here we have an interesting result with the Intel Xeon E-2288G and its 8 cores and 16 threads offering better single and multi-threaded performance than the E-2286G. One could probably guess this from the spec sheet, but it is nice to see confirmation of this hypothesis.
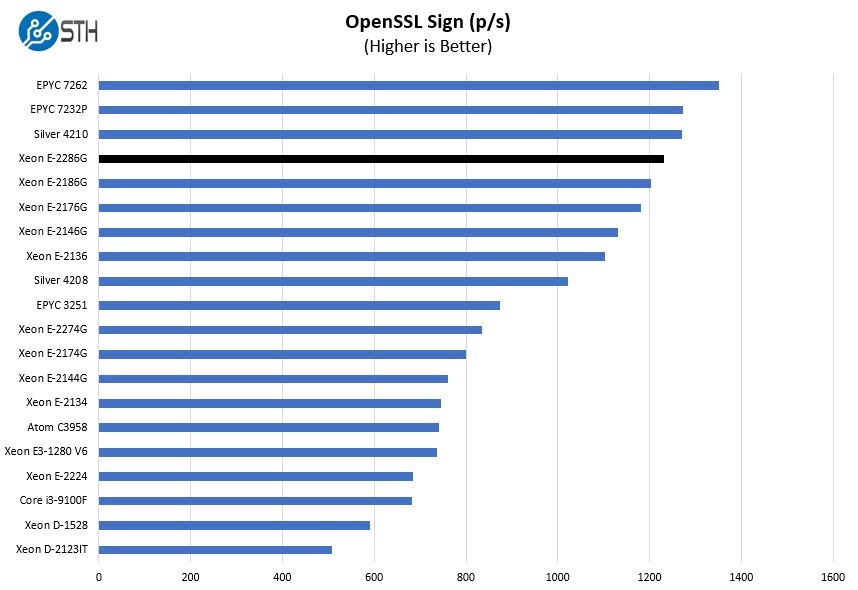
OpenSSL Performance
OpenSSL is widely used to secure communications between servers. This is an important protocol in many server stacks. We first look at our sign tests:
Here are the verify results:
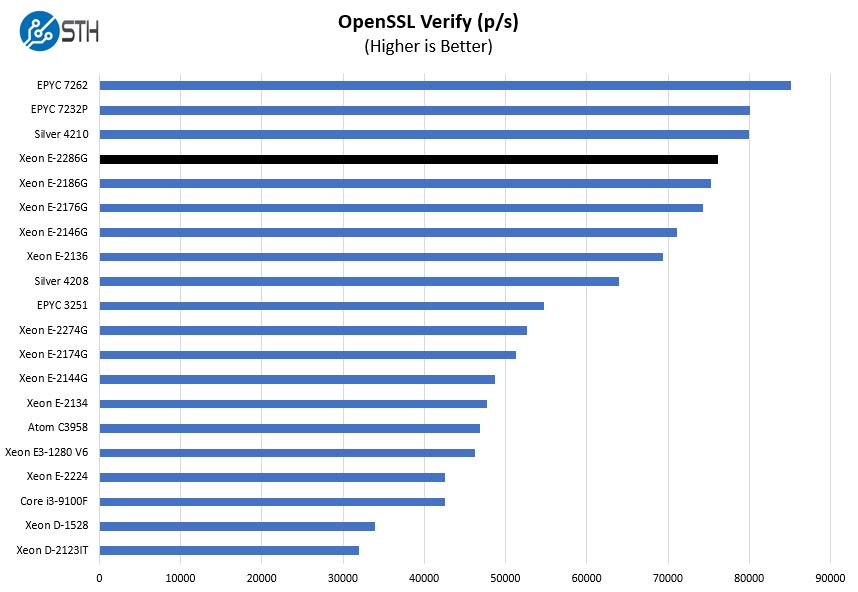
AMD generally does not try to compete in this space, but we did want to point out the AMD EPYC 7232P. The CPU and platform cost a bit more than the Intel Xeon E-2286G. At the same time, the EPYC 7232P is in a different class in terms of expandability and usually offers better performance. If you are trying to build a system with a large number of disks, NICs, or accelerators, yet need minimal processing power, the EPYC 7232P is a considerably more robust platform. If you are getting 2:1 or 3:1 consolidation ratios due to the I/O side, that cost delta becomes very small.
UnixBench Dhrystone 2 and Whetstone Benchmarks
Some of the longest-running tests at STH are the venerable UnixBench 5.1.3 Dhrystone 2 and Whetstone results. They are certainly aging, however, we constantly get requests for them, and many angry notes when we leave them out. UnixBench is widely used so we are including it in this data set. Here are the Dhrystone 2 results:
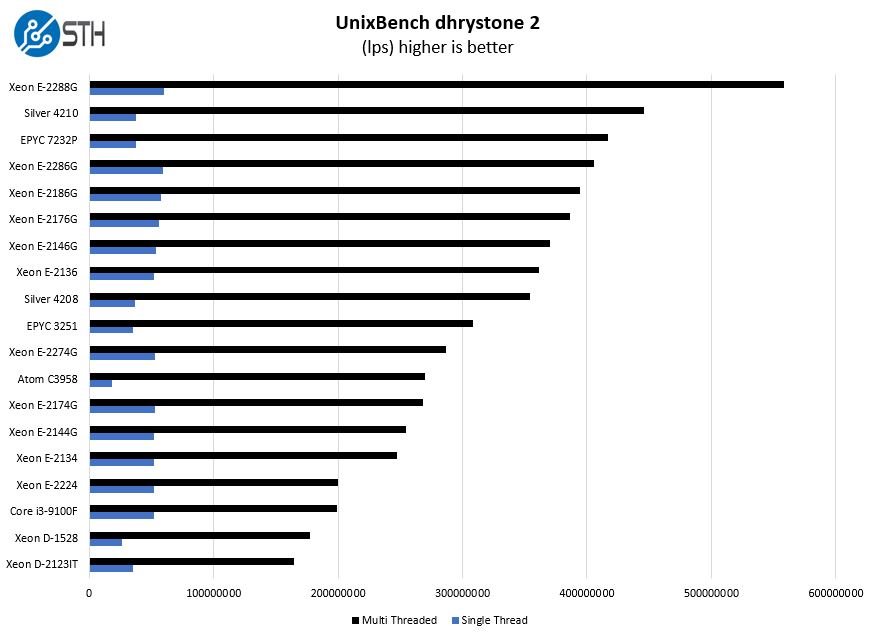
Here are the whetstone results:
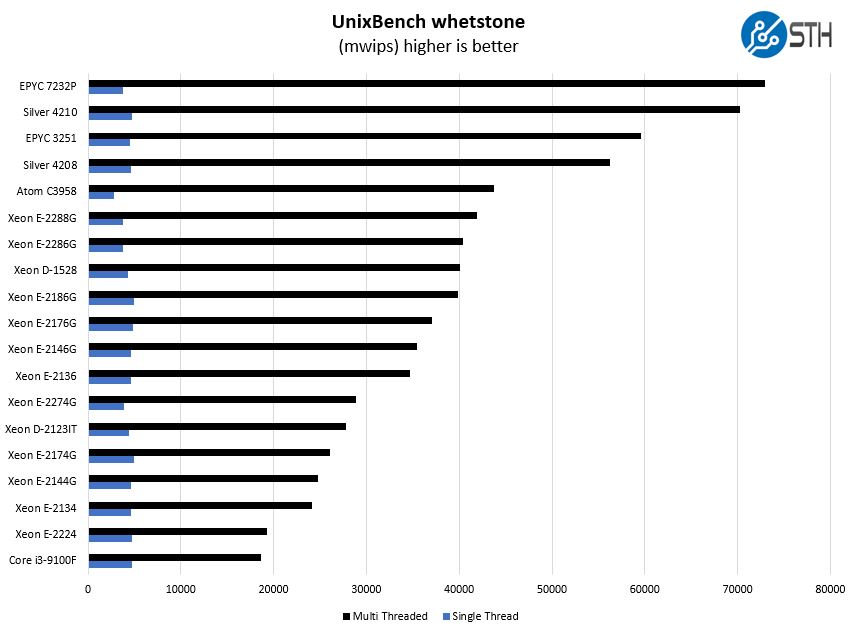
You will also notice here that the Intel Xeon E-2286G outpaces the six core embedded parts such as the Intel Xeon D-1528 by a large margin.
GROMACS STH Small AVX2/ AVX-512 Enabled
We have a small GROMACS molecule simulation we previewed in the first AMD EPYC 7601 Linux benchmarks piece. In Linux-Bench2 we are using a “small” test for single and dual socket capable machines. Our medium test is more appropriate for higher-end dual and quad-socket machines. Our GROMACS test will use the AVX-512 and AVX2 extensions if available.
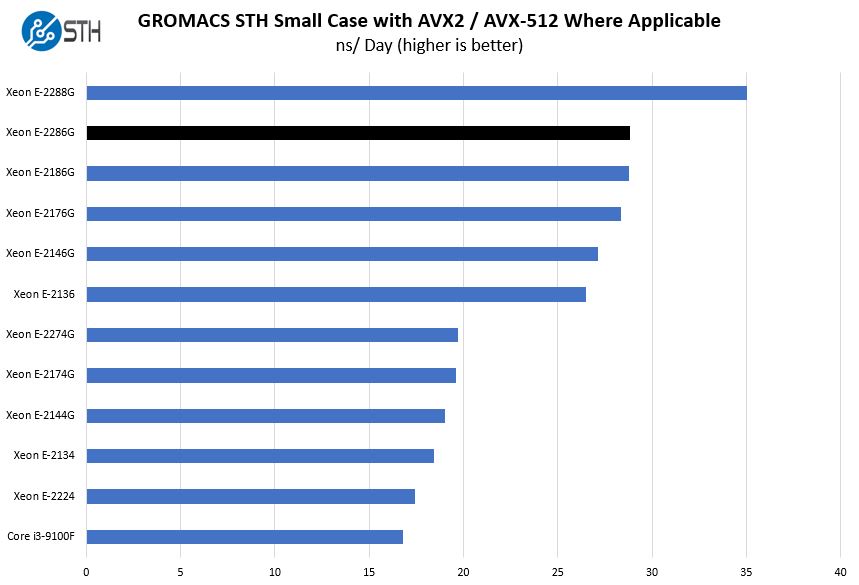
When we are using AVX pipelines, the generational improvement is much smaller. We see very similar performance between the Xeon E-2286G and the Xeon E-2186G.
Chess Benchmarking
Chess is an interesting use case since it has almost unlimited complexity. Over the years, we have received a number of requests to bring back chess benchmarking. We have been profiling systems and are ready to start sharing results:
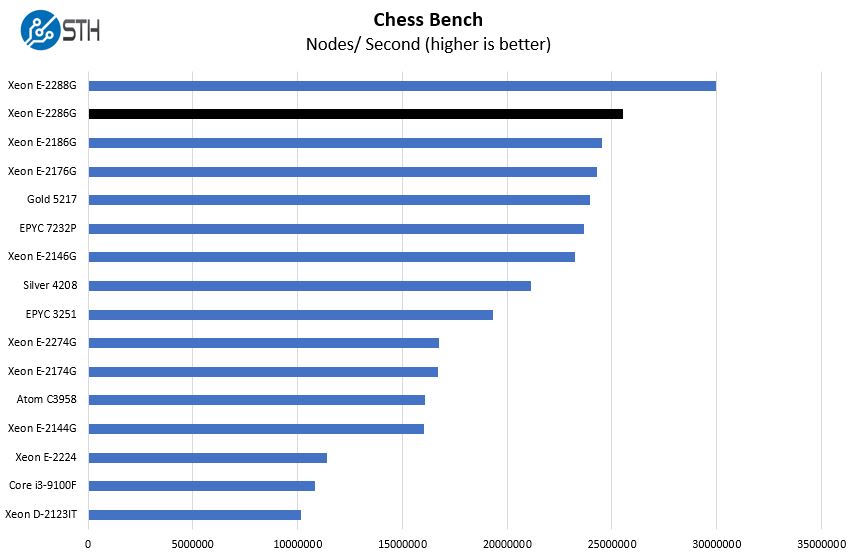
On our chess benchmark, we pulled in the Intel Xeon Gold 5217 where the Intel Xeon E-2286G is noticeably faster even at a small fraction of the price. If you are looking at the lower-core count Xeon Scalable and can fit in the I/O, memory, and single CPU footprint of Xeon E, then one can see significant cost savings.
Next, we are going to have power consumption, market positioning, and our final words.



