Our Intel Xeon E-2276G benchmarks and review finds a processor that is an incremental improvement over the previous generation. We also find a break from a trend that we often see in the range where the new updated SKU is a full increment better versus the previous generation. Still, there is improvement year-on-year which is great for users in the market.
Key stats for the Intel Xeon E-2276G: 6 cores / 12 threads with a 3.8GHz base clock and 4.9GHz turbo boost. There is 12MB of onboard cache. The CPU features an 80W TDP. These are $362 list price parts. Here is the Intel Ark page for your reference.
Here is what the lscpu output looks like for an Intel Xeon E-2276G:
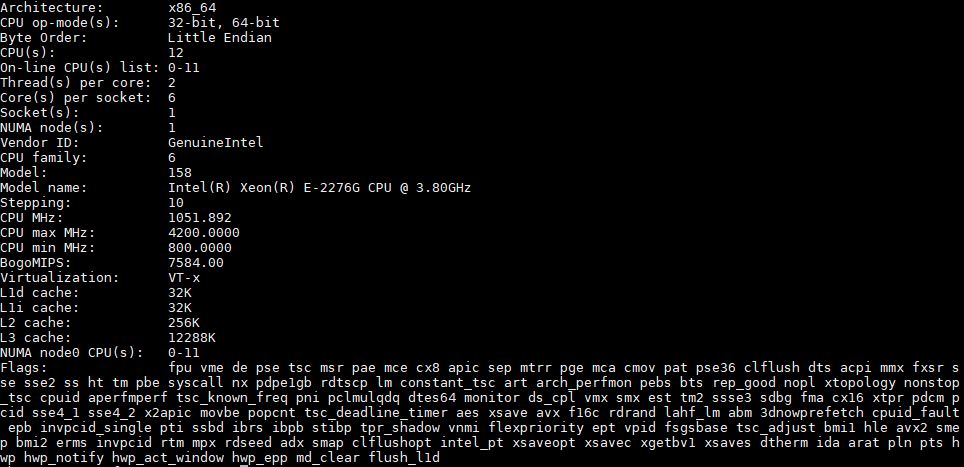
If you read our Intel Xeon E-2286G Benchmarks and Review article, and then see these specs, it may seem that they are very similar. They are except for three items:
- The Xeon E-2276G has slightly lower clocks.
- The price is around $70 less.
- Perhaps most importantly, the TDP is 15W lower.
We are going to look at the first and third of those in our benchmark section. We are then going to see how that translates to value in our market analysis section.
One of the biggest benefits to the Intel Xeon E-2276G is the “G” which denotes onboard graphics. For those that need a server that can do video encoding/ transcoding, having onboard graphics is important.
We are also making a major change with the latest Xeon E-2200 reviews, starting with this article. Our charts now have 16 examples in these sockets from the previous and current generations. As a result, we are only mixing in a very small set of other processors to give some indication where performance falls compared to other lines. Realistically, if you are buying or upgrading a Xeon E-2200 series server, you are choosing between processor options that can be used in that server. Since that is a key decision point we are targeting with this series, we are going to primarily focus on in-socket comparisons.
Test Configuration
Here is our basic configuration for this class of CPU:
- Motherboard: Supemicro X11SCA-F
- CPU: Intel Xeon E-2276G
- RAM: 4x 8GB DDR4-2666 ECC UDIMMs
- SSD: Intel DC S3710 400GB
- SATADOM: Supermicro 32GB SATADOM
The CPU itself supports up to 128GB of RAM, in a 4x 32GB configuration. We see these platforms using 32-64GB or less given cost sensitivities.

There are going to be folks who want to point to AMD alternatives. As of this writing, there are really no alternatives in this space because while AMD may have competitive CPU parts, vendors have a vibrant Intel Xeon E-2100/ E-2200/ Core i3 ecosystem. AMD needs to do some work here to catch up, but it is not a focus market for them. Single socket servers in this segment are a relatively low volume area.
Next, we are going to take a look at our Intel Xeon E-2276G benchmarks, we are then going to focus on power consumption then conclude with our final words on the processors.




And some other ones:
Intel last night made public two more data leakage disclosures, which tie back to Zombieload and November’s TAA issue.
Here are the new disclosures:
CVEID: CVE-2020-0548
Description: Cleanup errors in some Intel(R) Processors may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable information disclosure via local access.
CVSS Base Score: 2.8 Low
CVE-2020-0549
Description: Cleanup errors in some data cache evictions for some Intel(R) Processors may allow an authenticated user to potentially enable information disclosure via local access.
CVSS Base Score: 6.5 Medium
CVE-2020-0548 is referred to as Vector Register Sampling and CVE-2020-0549 is going as L1D Eviction Sampling.
A speculative execution side channel variant known as L1D Eviction Sampling may allow the data value of some modified cache lines in the L1 data cache to be inferred under a specific set of complex conditions.
L1D Eviction Sampling is to be mitigated by new CPU microcode updates.
A speculative execution side channel variant known as Vector Register Sampling may allow the partial data values of some vector operations to be inferred under a specific set of complex conditions that include vector operations executing after a period of vector inactivity.
The award for the best use of Lego Minifigs in an IT component review goes to…. John Lee and STH!