This week, the Intel Data Streaming Accelerator or Intel DSA was launched. A major challenge in the silicon designs of tomorrow is how to move data around increasingly complex systems. That data movement uses an enormous amount of power in modern servers and can be the source of significant performance bottlenecks. A great example of this is in the AI accelerator space where just about every company is looking to build compute units with nearby cache memory to ensure that even trips to DRAM are minimized. Against this backdrop, the Intel DSA is designed to increase performance for data mover and transformation operations.
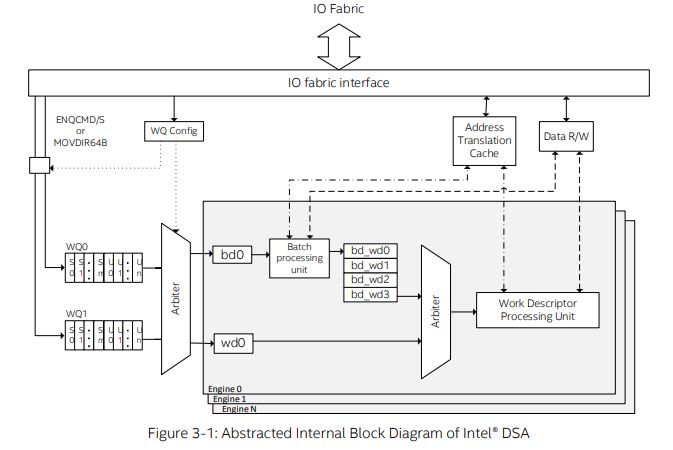
Intel Data Streaming Accelerator (DSA)
Intel DSA accelerates data mover capability when dealing with volatile memory, persistent memory (e.g. Optane DCPMM), memory-mapped I/O, NTB devices, and remote node memory. The new Intel DS also supports transformation operations on memory. From Intel’s release, these include:
- Generate and test CRC checksum, or Data Integrity Field (DIF) to support storage and networking applications.
- Memory Compare and delta generate/merge to support VM migration, VM Fast check-pointing and software-managed memory deduplication usages. (Source: Intel)
Also from Intel’s release, the DSA supports a variety of PCI-SIG defined services including:
- Address Translation Services (ATS)
- Process Address Space ID (PASID)
- Page Request Services (PRS)
- Message Signalled Interrupts Extended (MSI-X)
- Advanced Error Reporting (AER)
(Source: Intel)
Integrating the Intel Data Streaming Accelerator (DSA)
When we talk about accelerators, we often discuss PCIe devices like GPUs. Since the DSA is designed to be exposed as a PCIe endpoint, one may automatically jump to that conclusion. Instead, the DSA is designed to be embedded in the chips that Intel produces. Instead of an external accelerator, it is better to think of these as an internal accelerator like AES-NI.
Intel says that its SoCs can support multiple Intel DSA device instances. These DSAs can not only exist on one chip, but are designed to be found on more than one server chip. Intel uses “SoC” instead of CPU, so this is certainly something we could expect to be in the company’s products outside of the Xeon range.
Final Words
To give you some idea of where these can be used, it can be used to help offload memory copying and zeroing form the CPU and data copy in virtual switching. This is one of those technologies that looks like it will be implemented in future Xeons. Enabling more efficient memory operations is going to be important to get more performance in future servers.