Alongside AMD’s slew of consumer-related product announcements with desktop and mobile Ryzen processors, the company also took a moment of its time during its CES 2026 presentation to address the embedded market. The tangentially-related cousin to the consumer market, AMD’s embedded lineup of processors are aimed at the automotive and industrial markets, as well as any other device manufacturers who are building a non-PC edge device and want a chip with more long-term support.
Noteworthy for its trailing design schedule that favors reliability over timeliness, AMD’s embedded processors are normally the last families of chips to get upgraded with the newest CPU and GPU architectures. Which is to say that with AMD now more a than a year past the launch of the Zen 5 architecture, the Ryzen Embedded lineup is due for an upgrade to Zen 5 generation hardware. And that is exactly what AMD is announcing today at CES 2026 with the reveal of the Ryzen AI Embedded series of chips.
Taking a page from AMD’s Ryzen AI consumer chips, the latest generation of Ryzen parts for the embedded market is getting the same AI branding – underscoring the inclusion of an XDNA 2 architecture NPU, as well as the value AMD places on it. It also reinforces the similarities in terms of hardware, as AMD will be reusing a lot of their mobile silicon for these Ryzen AI Embedded processors.
| AMD Ryzen Embedded Generations | ||||
| CPU Arch | GPU Arch | NPU Arch | Silicon | |
| Embedded 8000 | Zen 4 (up to 8 cores) | RDNA 2 | XDNA (1) | Phoenix |
| AI Embedded P100 | Zen 5 (up to 12 cores) | RDNA 3.5 | XDNA 2 | Krackan Point / Strix Point |
| AI Embedded X100 | Zen 5 (up to 16 cores) | RDNA 3.5 | XDNA 2 | Strix Halo |
Altogether, AMD is announcing a pretty deep stack of parts for the Ryzen Embedded market. They are not just supplanting the current Ryzen Embedded 8000 series chips, but they are expanding the Ryzen Embedded portfolio overall. For this generation of chips there will be two different sub-series of chips: the P100 series of chips for more lightweight use cases, as well as the forthcoming X100 series for more heavyweight use cases such as physical AI. And even the P100 is technically being split into two lineups – a set of 4 & 6 CPU core chips launching today, and a set of more powerful chips with up to 12 CPU cores that is launching at some later point in the first half of this year.
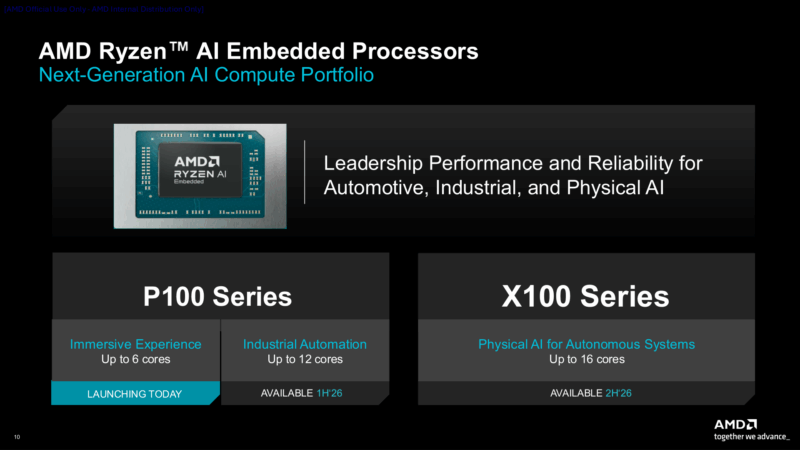
Ryzen AI Embedded P100: Up to 6 Zen 5 CPU Cores & 50 TOPS NPU
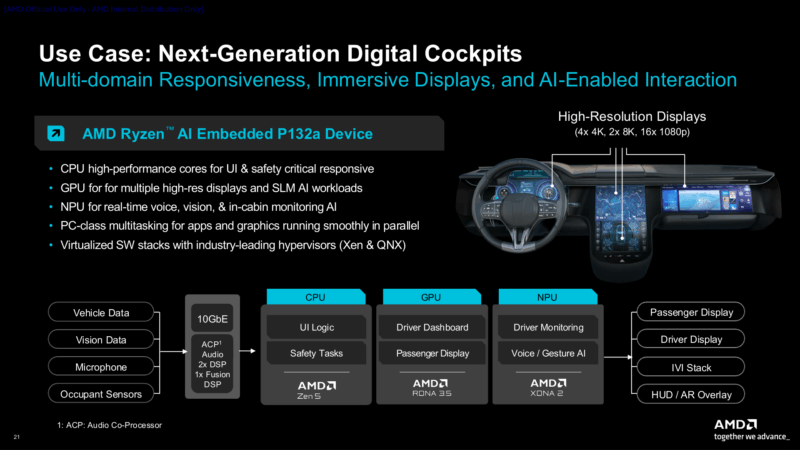
For today’s announcement the focus is on AMD’s first group of P100 chips. 6 SKUs in all – split up between regular, industrial, and automotive customers – the 4 and 6 core P100 chips are set to bring AMD’s latest and greatest mobile architectures to the embedded market. That includes the Zen 5 CPU architecture, RDNA 3.5 GPU architecture, and AMD’s XDNA 2 NPU architecture.
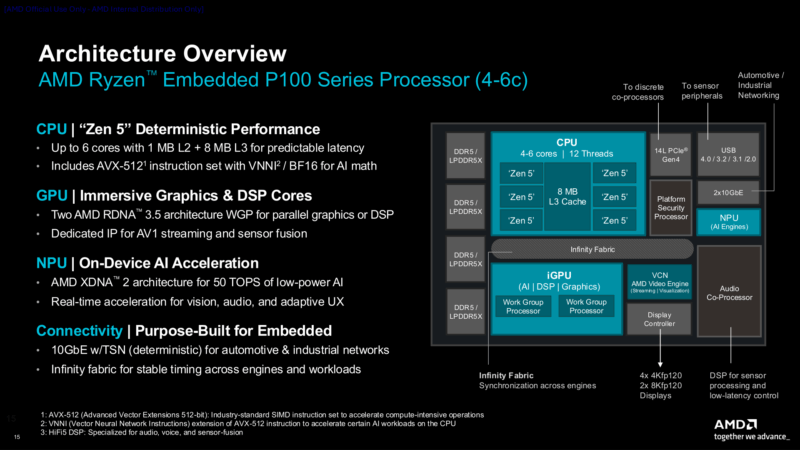
From a high level, the chip almost appears to be a dead-ringer for AMD’s Krackan Point hardware, which is currently used in lower-end chips like the Ryzen AI 5 340, a similar 6 core chip featuring the same graphics and AI capabilities as the fastest P100 SKU.
But I say “almost” because there is one curious item here that is not found on AMD’s consumer chips: dual 10Gb Ethernet ports seemingly emanating from the SoC itself. Unfortunately, we have not had a chance to chase down further information from AMD to get confirmation on how this is implemented, but perhaps their Strix Point and Krackan Point silicon have been hiding an extra feature all along?
In any case, Krackan Point hardware would represent a significant step up from the Phoenix silicon used in the existing Ryzen Embedded 8000 series. Besides the more performant CPU cores, this also factors in the much newer RDNA 3.5 architecture that can drive multiple 8K/120Hz displays. And for workloads that can tap the NPU, the XDNA 2 NPU used in this silicon is over triple the performance of the 8000 series trip. And the gains versus even older Ryzen Embedded chips are even greater – with AMD’s marketing department favoring those comparisons at CES 2026.
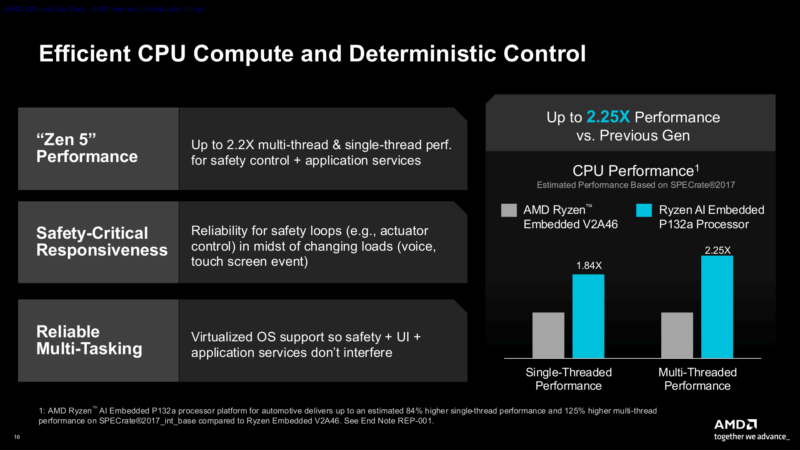
Otherwise, for readers who know their Ryzen AI mobile chip specs, this embedded lineup all looks quite similar. The chips have a TDP range of 15W to 54W, support LPDDR5X memory, and are BGA-soldered chips using the same 25mm x 40mm FP8 BGA socket as we have seen elsewhere.
Consequently, the big difference for this product lineup is not the hardware itself, but rather the reliability and support that come from being embedded-class processors. AMD is rating the P100 series for 10 years of 24/7 operation, and further variants of these chips will be validated to operate at extreme temperatures.
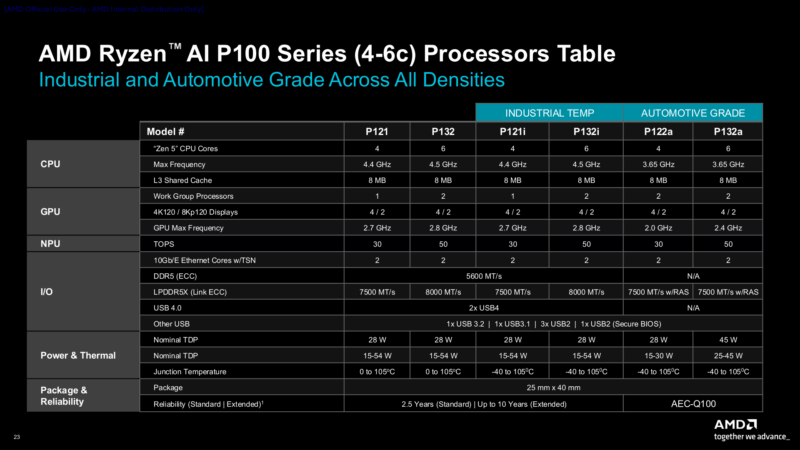
Altogether, AMD is providing 6 SKUs, which are essentially the same two chips with additional temperature and automotive grade validation. The low-end of the P100 family is the Ryzen AI Embedded P121, which features 4 Zen 5 CPU cores running at a peak clockspeed of 4.4GHz, a single Radeon Work Group Processor (2 GPU cores), and a reduced performance 30 TOPS NPU. Its higher-performing counterpart is the P132, a 6 CPU core chip peaking at 4.5GHz with 2 Radeon WGPs (4 GPU cores) and a full-performance 50 TOPS NPU. Both chips have a nominal TDP of 28 Watts, but as mentioned earlier can be configured up or down between 15W and 54W as a manufacturer needs.
The wider temperature range version of these chips will be the P121i and P132i respectively. Both are feature identical to the base chips, but are validated for operation below freezing temperatures, down to -40 degrees (Celsius or Fahrenheit, take your pick).
Finally, AMD’s automotive grade Ryzen AI Embedded chips are bigger outliers. Strictly speaking, there is no automotive equivalent of the P121; instead, we get the P122a. This is still a 4 CPU core chip, but it gets the same higher-performance 2 WGP configuration as the more powerful chip. Meanwhile the P132a looks more like an automotive-validated version of the P132. Notably, both of the automotive chips ship with slower CPU and GPU clockspeeds and ditch some features like USB4 support, instead trading that for RAS support.
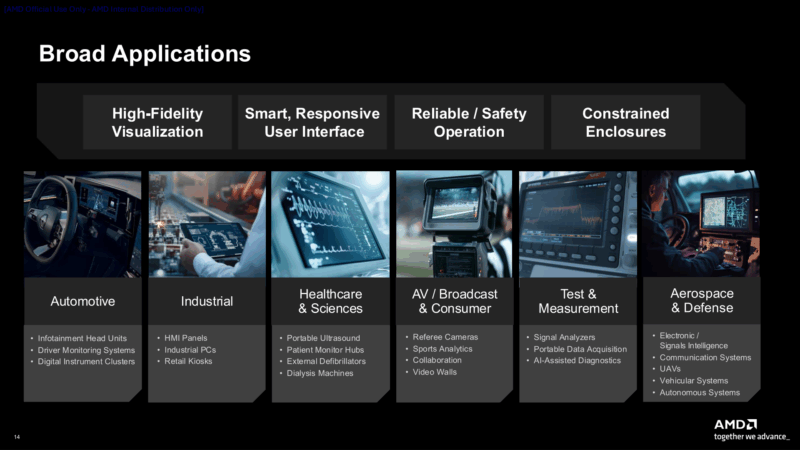
Ultimately, these chips will be destined for a wide variety of devices. Besides automotive use cases – which is certainly one of AMD’s big pushes at this time – the company is also aiming them at broadcast equipment, industrial PCs, kiosks, medical devices, and even aerospace. So AMD has a pretty broad market in mind.
Per today’s official launch, P100 hardware samples and associated software are available now to AMD’s partners. Meanwhile proper P100 production will ramp up in the second quarter of this year, with reference boards to follow in the second half of the year.





Congratulations to all success
Honestly… The big missing feature from any of the spec sheets is PCIe lanes.
If these had say 16-24 PCIe lanes, they would make amazingly performant low power SSD NAS solutions for the Prosumer/SMB space.