The GL.iNet GL-MT6000 or the Flint 2 is a WiFi router that was surprising when we found the chipset it is running. Inside, it has the MediaTek MT7986AV, which is the same processor found in the BPi-R3 Mini at just a slightly higher price ($139. We had a Banana Pi R3 Mini Kit (Amazon Affiliate) in our cart to build an OpenWRT test platform with, but then realized that the Flint 2 was a similar price at $139, with some hardware upgrades and a nicer design, so it seemed like a better idea. As a result, we bought a Flint 2, found OpenWRT running underneath the GL.iNet firmware, and then put the device through our new network testing.
If you just want to check current pricing or buy a GL-MT6000 Flint 2, here is an Amazon affiliate link.
GL.iNet GL-MT6000 Flint 2 Hardware Overview
This is the WiFi 6 generation router, but given it has 2.5GbE we wanted to test it with our wired testing suite.

The antenna array lifts into place making the front of the unit look like many others with a lot of vents and a box with antenna towers at the rear.

On one side we get vents.
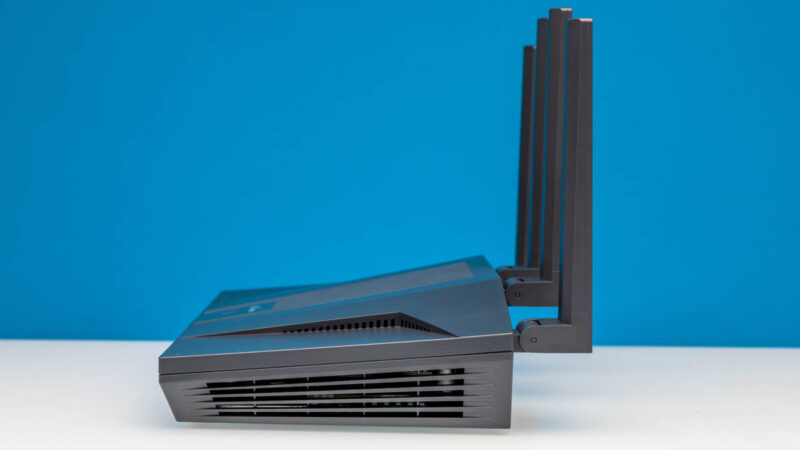

On the other side we get vents and the USB 3.0 Type-A port.

This can be for storage or used for attaching a WWAN modem.

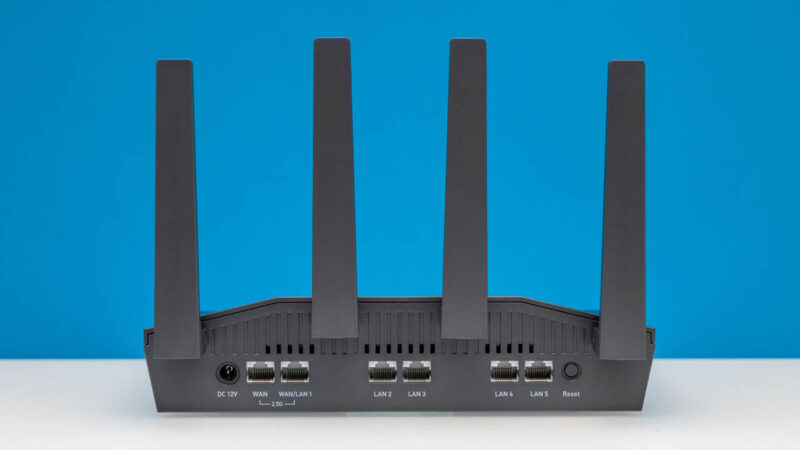
On the rear is where we find most of what is going on. There are two 2.5GbE ports, one for WAN, and one that can be either another WAN Port or LAN1. We configured this as one 2.5GbE WAN and one 2.5GbE LAN port. There are four additional 1GbE LAN ports, a 12V DC input, and a reset button.

On the bottom, we find vents, the login information, rubber feet, and mounting points.

Inside this is a MediaTek MT7986AV chipset solution, the same as we wanted to get anyway in the BPi-R3 Mini setup. There is also a MT7531AE switch inside that is handling the 1G LAN port connetivity. We are keeping this one closed since we are using it to test our future WiFi testing setup.
Next, we are going to switch it up a bit. Instead of going to the GL.iNet management interface, we wanted to show the OpenWRT LuCI management interface.
GL.iNet GL-MT6000 Flint 2 OpenWRT LuCI Management
We will get to the default GL.iNet interface on the next page, but one of the more interesting aspects of this is that in Advanced Settings, you can enable LuCI which is widely used for managing OpenWRT devices.
It took a few seconds to open, but once we were there, we could see we are running OpenWRT 21.02. There is even a page on the OpenWRT Wiki on this device.
Here you can do things like Wireless Channel Analysis.
You can setup the firewall.
And firewall zones.

You can even do things like install packages. Realistically, if you just wanted to manage this as an OpenWRT device, you can. Still, GL.iNet has its management interface on this device as well, so let us get to that.





They’re underselling this. It’s known as the best WiFi 6 OpenWRT hardware out. https://www.reddit.com/r/openwrt/comments/1lopamn/current_highest_spec_router_that_supports_openwrt/
You’re right on the price now. If it goes on sale it’s the same or cheaper than that bpi kit you linked
This is also known for having really top tier wifi. I know you don’t test wifi, but it’s the best out there
Unfortunately it doesn’t come with PoE …
As someone who uses and develops for OpenWrt a lot, I have to add that this is a custom modified fork of OpenWrt, that’s also why it’s stuck at the very outdated 21.02 release which hasn’t received security patches in years.
However, OpenWrt itself provides full up-to-date support for the device, and OpenWrt images can be installed by simply flashing the respective sysupgrade image, as linked on the wiki page.
Devices with Mediatek Filogic chipset are generally very well supported by OpenWrt and perform great.
I’ve had a flint2 for nearly a year at this point and have enjoyed the simplicity of setting it up and the ability to integrate tailscale into it without issue
@Joe routers don’t typically come with PoE, mikrotik is an outlier for that. If you need PoE
you’d be better off getting a basic PoE switch or a PoE injector
My only problem is that this is a Hong Kong based company, not a US based company. I get that everything is MIC but I prefer to buy something designed in US, Japan, or some other non-life threating county.
I’d love to see, with Ryan Smith here (welcome!), to a return of AnandTech’s charts. Meaning to say, each router review will just add another bar to the chart with all the previous results.
This may take time to ensure a standard methodology (otherwise, they can’t be plotted on the same graph!), though, but hopefully the old routers can be re-tested.
This is pretty amazing equipment STH has and it’d be great to have a unified methodology + charts / database.
I thought the $280 UCG-Fiber was “just OK” with just ~1500 users, but seeing these $100 – $140 devices only achieving ~100 users seems like the UCG-Fiber has more oomph.
As mentioned by the other comment, they’re using a custom version of OpenWRT based on an older version. It would be interesting to see if installing the version from OpenWRT would cause any changes in performance.
Flint 3 with WiFi7 would be way more interesting.
For 199$ not even that much more.
you should went with OpenWRT 24 flavor of Gl-Inet firmware (available from their website), I got better results on my VPN use (~100Mbps more bandwidth over Wireguard) + nice feature of multiple VPN active at the same time and routing traffic between them. All in all, great device for the money. Wanted to move to their Flint 3 but as it actually has weaker CPU it didn’t work for me due to lower Wireguard speeds. Cheers!
I have had two of these routers for more than a year, and I love that I can do whatever I want in LuCI: set-up VLANs, install additional packages, make my own dual-WAN script, etc. But they both have one, I believe physical, downside – low-sensitivity of the 2.5G ports, if the cable is longer than ~50m they can’t negotiate it even at 1G.